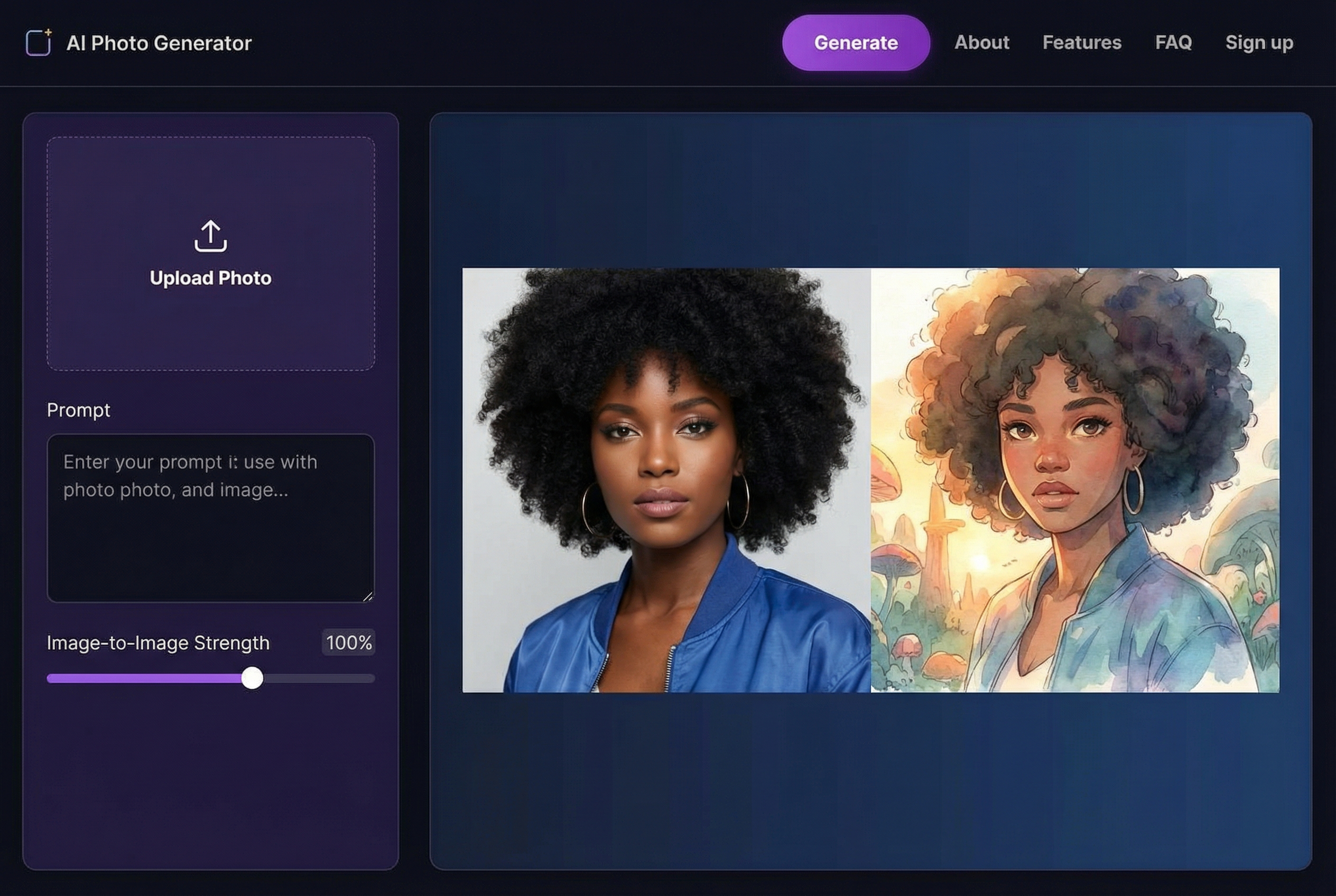
So, what is generative AI? In simple terms, it’s a type of artificial intelligence that can create entirely new content. We’re talking about fresh text, images, code, and even music that didn’t exist before.
It’s a huge leap from traditional AI, which mostly just analyzes or sorts data that’s already there. Generative AI actually generates something original. Think of it less like a calculator and more like a creative partner.
Understanding the "Generate" in Generative AI
Let's use an analogy. Imagine you have two assistants.
The first is like a master librarian. They can find any book you ask for, sort them perfectly by genre, and tell you which ones are the most popular. This is your classic AI—amazing at organizing and analyzing information that already exists.
Now, imagine a second assistant: an imaginative storyteller. After reading every single book in that library, this assistant can write a brand-new story in the style of your favorite author, complete with unique characters and unexpected plot twists. That is generative AI. It doesn't just fetch information; it synthesizes everything it knows to produce something completely original.
This creative spark is what sets it apart. It’s not just about identifying a cat in a photo; it’s about creating a picture of a cat that has never existed—maybe one wearing a tiny astronaut helmet, floating through space.
The Shift From Analysis to Creation
The real difference comes down to the job at hand. Traditional AI systems are built for what we call discriminative tasks—their main job is to tell things apart.
For example:
- A spam filter decides if an email is "spam" or "not spam."
- A recommendation engine predicts whether you'll "like" or "dislike" a movie.
- Facial recognition determines if a face "matches" or "does not match" a known identity.
Generative AI, on the other hand, is all about generative tasks. It digs into the underlying patterns and structures of data to generate new, synthetic data that looks just like the real thing. It’s a move from simple classification to full-blown creation.
To make this distinction crystal clear, let's break down the core differences in a simple table.
Generative AI vs Traditional AI At a Glance
This table quickly highlights how these two types of AI operate in fundamentally different ways.
| Capability | Generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT, Midjourney) | Traditional AI (e.g., Spam Filter, Recommendation Engine) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Creates new, original content | Analyzes and classifies existing data |
| Core Task | Generation (What could this be?) | Discrimination (Is this A or B?) |
| Output | Novel text, images, code, music | Predictions, classifications, recommendations |
| Example Goal | "Write a poem about the ocean." | "Is this email spam?" |
| Complexity | Generally higher; requires understanding context and structure | Generally lower; focused on pattern recognition for classification |
As you can see, one is a creator, and the other is an analyst. Both are incredibly useful, but generative AI has unlocked a whole new world of possibilities.
Why Is This So Important Now?
The buzz around generative AI isn't just hype; it marks a massive leap in what computers can do. This isn't a small step forward—it's fueling a huge economic shift. The global generative AI market is projected to skyrocket from $25.86 billion to around $1 trillion by 2034. You can dig into more of the numbers on this growth over at Precedence Research.
This explosion is happening because these tools can now handle complex, creative work that we once thought only humans could do.
At its heart, generative AI is a probability machine. Given a prompt, it calculates the most likely next word, pixel, or musical note to create a coherent and novel output.
This ability to churn out high-quality, original content is changing entire industries. Marketers can generate ad copy in seconds, developers can write code faster with AI assistants, and artists can explore new visual concepts at an incredible pace.
For you, this means tools like AI Photo HQ can generate professional-grade photoshoots without ever needing a camera. You can turn a simple text description into a stunning, realistic visual. It’s not about replacing human creativity, but amplifying it—giving everyone the power to bring their ideas to life.
How Generative AI Actually Works
To really get what generative AI is all about, you have to peek under the hood at the engines driving it. Don't worry, you don't need a degree in computer science. The core ideas are actually pretty intuitive once you have the right analogies.
At its heart, all generative AI follows a simple three-step rhythm: it digests a mind-boggling amount of data, a model is trained to recognize all the patterns in that data, and then it uses that training to spit out something totally new.
This is the basic flow, from raw data to a finished piece of content.
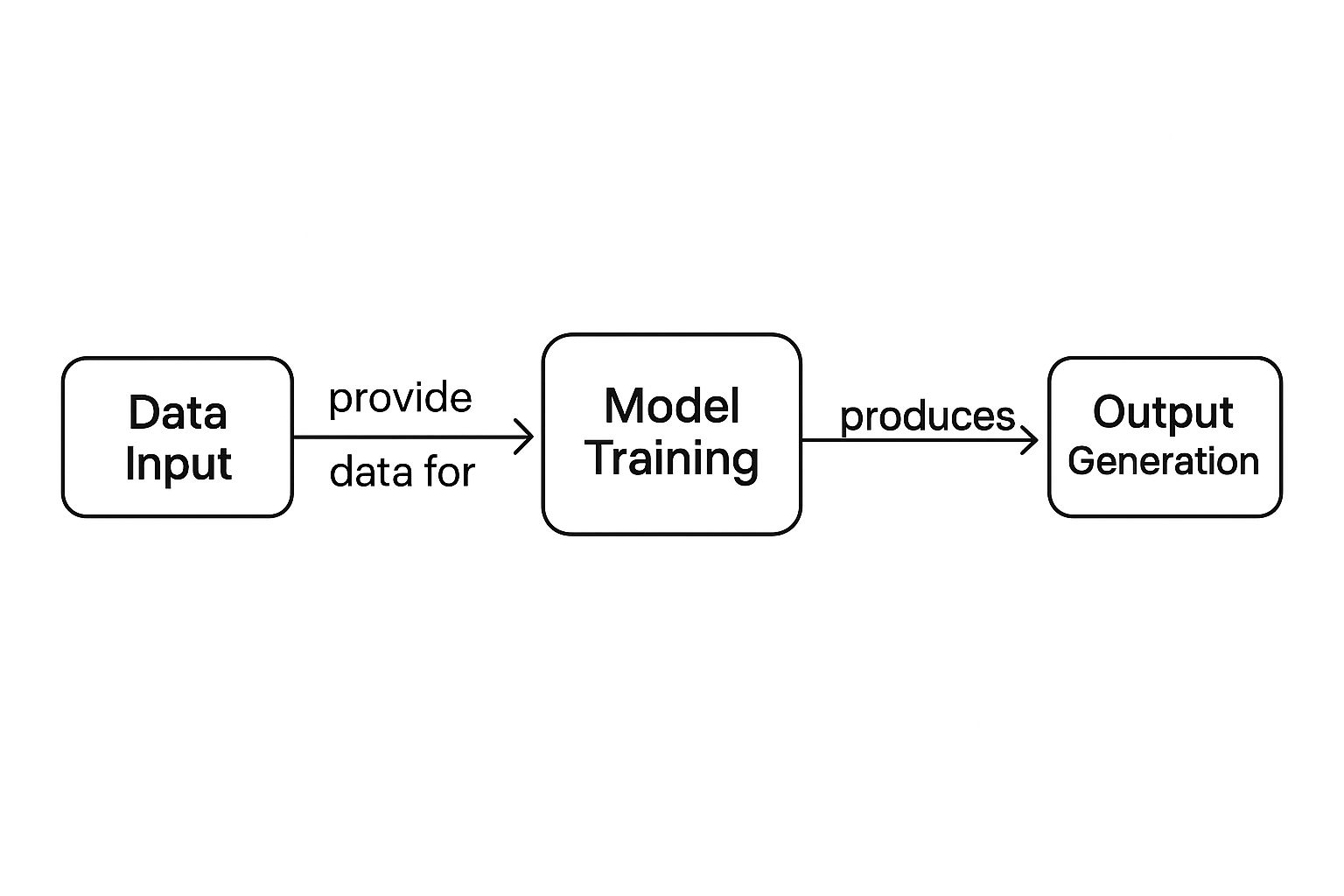
This fundamental process is the launchpad for all the different kinds of models that do specific creative things, like writing an email or dreaming up an image.
Large Language Models: The Ultimate Predictors
Large Language Models, or LLMs, are the brains behind text-based AI like ChatGPT. Think of an LLM as the world's most sophisticated predictive text system. Your phone tries to guess the next word you're going to type; an LLM tries to predict the next word, sentence, and paragraph based on the patterns it learned from practically the entire internet.
When you feed an LLM a prompt like, "Write a story about a brave knight," it doesn't actually "understand" what a knight is or what it means to be brave. Instead, it's all a game of probabilities.
- Breaking Down the Prompt: It first chops up your request into mathematical pieces called tokens.
- Searching Its Brain: The model then scans its massive library of training data—books, articles, websites—to find every pattern associated with "brave" and "knight."
- Making a Prediction: It calculates the most likely word to come next. For stories, "Once" is a pretty safe bet, so it starts there.
- Building the Chain: After "Once," it predicts "upon," then "a," then "time." It keeps chaining these predictions together, word by word, to build out a story that makes sense.
What you get is a brand-new story that feels familiar because it's built from the same patterns found in all the stories the AI has already read.
Generative Adversarial Networks: The Artistic Duel
Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs, are a wild concept often used to create hyper-realistic images. The best way to think about it is as an endless competition between two AIs: a master art forger and a sharp-eyed detective.
- The Generator (The Forger): This AI's only goal is to create fake images. Its first attempts are laughably bad, nothing more than digital noise.
- The Discriminator (The Detective): This AI's job is to look at a mix of real images and the forger's fakes and call out which is which.
This constant back-and-forth forces both AIs to get smarter over time.
The forger creates an image and shows it to the detective. "Fake!" the detective shouts, giving feedback on why it looks wrong. The forger listens, tries again, and produces something a little more convincing. This happens millions of times.
This competitive loop is what makes GANs so powerful. The Generator gets progressively better at creating convincing fakes, while the Discriminator gets better at spotting them. The process ends when the Generator's creations are so good that the Discriminator is fooled about 50% of the time.
By that point, the Generator has essentially become a master artist, capable of producing stunningly realistic and original images from scratch.
Diffusion Models: The Digital Sculptor
Diffusion Models are the tech behind most of the popular AI image generators you see today, including the ones that power tools like AI Photo HQ. This process is less like a duel and more like sculpting—chipping away at a block of digital static to reveal a masterpiece inside.
Think of it like starting with a block of marble that's just random noise. A diffusion model is the sculptor who knows precisely how to chisel away that noise to reveal the statue hidden within.
Here’s a simplified look at how it works:
- Start with Pure Chaos: The process begins with an image of pure static, like an old TV with no signal. This is "noise."
- Get the Instructions: The model uses your text prompt—say, "a majestic lion in a field at sunset"—as its blueprint.
- Refine, Refine, Refine: In a series of steps, it methodically removes the noise, letting shapes, colors, and textures that match your prompt slowly emerge. It's like bringing a hopelessly blurry photo into perfect focus, one step at a time.
- The Final Image: After many passes, all the noise is gone. What's left is a crisp, high-quality image that matches your description.
This method gives users an incredible amount of control over the final image's detail and style. By tweaking how the "denoising" happens, you can get wildly different artistic results. If you want to go deeper on that, you can learn about Stable Diffusion sampling methods. It’s this careful, step-by-step refinement that lets generative AI create everything from photorealistic portraits to scenes straight out of a fantasy novel.
From Theory to Practice: 3 Generative AI Tutorials
Alright, let's ditch the robotic tone and get our hands dirty. Theory is great, but the real magic happens when you see generative AI actually do something useful. It's time to go from "what is it?" to "what can it do for me?"
I've put together three practical, step-by-step tutorials to show you just how powerful these tools are. By the end, you'll have some tangible results you can use right away.

We'll kick things off by whipping up some persuasive marketing copy. Then, we’ll dive into the visual world and create a stunning, original image from scratch. Finally, I'll show you how to make a lengthy document disappear into a neat, clean summary.
For each one, I'll give you the exact prompts and steps so you can follow along.
Tutorial 1: Generate Persuasive Marketing Copy
Generative AI is a natural at writing, but there's a catch: the output is only ever as good as your input. This is where the art of prompt engineering comes in. Think of a great prompt as a detailed creative brief you'd give to a human copywriter.
Let's say we're launching a new eco-friendly coffee brand called "EarthBrew" and need a quick Instagram post. A lazy prompt like, "Write an Instagram post for a new coffee brand," is going to get you a bland, generic result. It’s just too vague.
To get something great, you need to provide context, specify the tone, and give clear instructions.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Define Your Goal: Start with a clear objective. We want an engaging Instagram post that shouts about the brand's sustainable mission.
- Provide Rich Context: Give the AI the juicy details. What's the brand name? What makes the product special? Who are we talking to?
- Specify the Tone and Style: How should it sound? Tell the AI if you want it to be "upbeat," "passionate," or "professional." This sets the personality.
- Include a Call to Action (CTA): What do you want people to do after reading? Tell the AI exactly what to ask for.
- Request Formatting Elements: Don't forget the little things. Ask for emojis and hashtags to make the post pop on social media.
Here's a solid prompt you can tweak for your own needs:
Prompt: "Act as a social media copywriter. Write an Instagram post for a new coffee brand called 'EarthBrew.' The coffee is 100% organic, ethically sourced from small farms, and comes in compostable packaging. The target audience is environmentally conscious millennials. The tone should be upbeat, passionate, and inspiring. End with a call to action inviting people to try their first bag. Include 3 relevant emojis and 5 relevant hashtags."
Example Output:
"Ready to start your day with a coffee that tastes good and does good? ☀️ Meet EarthBrew! ☕️ Every cup is brewed from 100% organic, ethically sourced beans grown with love by our small farm partners. Plus, our packaging is fully compostable, so you can enjoy your morning ritual without the waste. 🌱 Join the movement for better coffee and a healthier planet. Try your first bag of EarthBrew today! #EarthBrew #SustainableCoffee #EcoFriendly #OrganicCoffee #MorningRoutine"
Tools are popping up everywhere to help with this. An AI social media content generator, for instance, can make short work of tasks just like this one.
The economic impact is staggering. The combined global market for generative AI software and services jumped from a mere $191 million to an incredible $25.6 billion in just two years. That explosion shows just how fast businesses are embracing AI to automate creative work and streamline their operations.
Tutorial 2: Create a Stunning AI Image
This is where the fun really begins. Image generation models, like the one that powers AI Photo HQ, can turn your words into visual art. The secret is learning to describe not just the what, but the how—the style, the lighting, the composition.
A vague prompt gives you a generic image. A detailed one creates something magical.
Let’s say you need a killer fantasy-themed image for a blog post.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Describe the Main Subject: Get specific. Don't just say "a castle." Try "an ancient, moss-covered stone castle." See the difference?
- Detail the Setting and Environment: Where is it? Paint a picture with your words, like "perched on a cliff overlooking a misty valley."
- Specify the Lighting: Lighting is everything for mood. Use phrases like "dramatic morning sunlight," "soft twilight glow," or "eerie moonlight."
- Define the Artistic Style: This is a big one. Do you want it to look "photorealistic"? Like a "vibrant digital painting"? Or maybe in the style of a "vintage comic book"?
- Add Composition and Detail Keywords: Use photography and art terms to guide the final look. Phrases like "wide-angle shot," "cinematic," "highly detailed," or "4K resolution" work wonders.
Here’s a prompt that pulls all these elements together:
Prompt: "Photorealistic image of an ancient, moss-covered stone castle perched on a cliff overlooking a misty valley. Dramatic morning sunlight breaks through the clouds, illuminating the scene. The style should be cinematic and epic, with a wide-angle shot that captures the grand scale. Highly detailed, 4K resolution."
Example Output:
The AI would crank out a breathtaking image that matches this perfectly—a majestic, detailed castle bathed in golden light, looking like it was pulled straight from a fantasy novel cover or a D&D campaign. This is a creative skill in itself, and you can dig deeper into how to write AI prompts to get even more spectacular results.
Tutorial 3: Summarize Long Documents Instantly
One of the most practical, day-to-day uses for generative AI is its knack for boiling down huge chunks of text into short, easy-to-read summaries. It's a massive time-saver for anyone—students, researchers, professionals—who needs to get the gist of a long report without reading every single word.
Imagine you've been handed a 10-page research paper on climate change and you need the key takeaways, like, now.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Set the Role: Tell the AI what hat to wear. Start with something simple like, "Act as a research assistant."
- State Your Goal Clearly: Be direct. "Summarize the following text for me." No need to be polite, just be clear.
- Specify the Output Format: This is the most important part. Do you want a single paragraph? A bulleted list of key findings? You need to tell it exactly what you're looking for.
- Paste the Text: After your instructions, just copy and paste the entire article or report.
Here’s a simple template you can adapt for almost anything:
Prompt: "Act as a research assistant. Please summarize the following article into five key bullet points. For each bullet point, provide a one-sentence explanation. Then, list the top three action items suggested by the text."
By structuring your request this way, you get way more than a simple summary. You get a clean, organized breakdown that's easy to digest and act on. You can turn a mountain of text into a handful of clear insights in seconds.
How Generative AI Is Actually Being Used in the Real World
So far, we've talked a lot about the 'what' and 'how' of generative AI. But beyond creating fun social media avatars or slick marketing copy, this technology is fundamentally reshaping entire industries. The concepts we’ve covered are the building blocks for some seriously high-stakes applications that are driving massive changes across the global economy.
Let's zoom out and look at how this is all playing out in the real world. From scientific labs to movie studios, generative AI is becoming a powerful sidekick, speeding up workflows and unlocking doors that were previously shut tight. It’s not just about doing things faster; it’s about doing things that used to be incredibly difficult, expensive, or even impossible.
Accelerating Science and Medicine
Think about drug discovery. Finding the right molecular structure for a new medicine is a notoriously slow and expensive process, often taking years and costing billions. Generative AI is flipping that script by designing and testing new molecules in a virtual sandbox at incredible speeds.
Scientists can now use AI models to generate thousands of potential drug candidates that have a high probability of working, which dramatically shortens that initial research phase. It’s like having a brilliant chemist on your team who can brainstorm and vet ideas 24/7.
The same idea applies to healthcare, where AI can generate synthetic patient data. This allows researchers to train diagnostic models to spot diseases earlier and more accurately, all without compromising the privacy of real patients.
Supercharging Software Development
For software developers, generative AI is like having an expert coder sitting right next to them. Tools built directly into their programming environments can suggest lines of code, write entire functions from a simple description, and even sniff out and fix bugs.
Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Code Generation: A developer might write a comment like, "create a function to validate a user's email address," and the AI instantly generates the code to do just that.
- Debugging Help: Instead of spending hours hunting down a tricky bug, a developer can paste the problematic code and ask the AI to find the error and suggest a fix.
- Learning on the Fly: It acts as an on-demand tutor, explaining complex programming concepts or even translating code from one language to another.
This doesn't make developers obsolete. Far from it. It frees them up from the tedious, repetitive parts of their job so they can focus on solving bigger, more creative problems.
Reshaping Media and Entertainment
The creative industries are in the middle of a massive shake-up, too. Generative AI is being used for everything from brainstorming movie scripts and creating concept art to producing final visual effects. In photography, for example, the ability to generate specific scenes and artistic styles is a total game-changer. You can dive deeper into how artificial intelligence is being used in photography to create stunning, tailor-made visuals.
Generative AI is also kicking open the door for new kinds of businesses, completely changing how content gets made and sold. A great example is people who are now learning about creating print on demand coloring books with AI.
The sheer scale of this adoption is wild. The market is exploding, supported by a talent pool of over 944,000 workers in key hubs like San Francisco, New York, and London. And with more than 8,700 patents filed globally, it's clear this isn't just a fad.
This boom shows we're way past the point of simple novelties. Generative AI is becoming a core piece of the economic engine. It’s helping businesses create personalized marketing campaigns at scale, design entirely new products, and even protect financial systems by generating synthetic data to train fraud-detection models. It connects the dots between a simple text prompt and a powerful, real-world business outcome.
Getting Real About AI's Strengths and Weaknesses
Generative AI is an incredible tool, there's no doubt about it. But like any powerful technology, it’s not magic. To really get the most out of it, you have to be honest about what it does well and where it falls short. On one hand, it can supercharge your productivity and unlock creative avenues you never thought of. On the other, it comes with some serious pitfalls that demand a smart, responsible approach.
Finding that balance is everything. It's the difference between using AI as a game-changing assistant and getting burned by its mistakes.

The Upside: What Generative AI Does Brilliantly
The wins you get from using generative AI are usually pretty immediate and obvious. It can slash the time you spend on tedious tasks, give you a creative spark when you're stuck, and help you connect with customers on a whole new level.
Here’s where it really shines:
- Huge Efficiency Boosts: Think about all the repetitive stuff that eats up your day—drafting emails, debugging code, or creating first-pass design concepts. AI can knock those out in seconds, freeing you up to focus on the bigger picture.
- A Cure for Creative Block: We've all been there, staring at a blank page. AI acts like a tireless brainstorming partner, spitting out hundreds of ideas, taglines, or visual styles to get your own creative juices flowing.
- Personalization on a Massive Scale: Before AI, creating truly personalized experiences for every single customer was a pipe dream. Now, businesses can generate custom marketing messages, product recommendations, and user journeys that make every interaction feel one-of-a-kind.
The Downside: The Gotchas You Can't Ignore
As exciting as the benefits are, generative AI is far from flawless. Its limitations aren't just minor quirks; they can cause real problems if you're not paying attention. Knowing these issues is the first step to using AI safely and effectively.
The biggest one to watch out for is something called an "AI hallucination." This is when a model confidently gives you an answer that is completely, totally wrong. It’s not lying in the human sense—it’s just assembling a response that looks statistically plausible, even if it has no basis in reality.
An AI hallucination is when the model just makes stuff up. It might invent a historical event, cite a scientific paper that doesn't exist, or even create a fake legal case to support its point, all while sounding completely authoritative.
This is exactly why you can never blindly trust AI-generated facts for anything important. Human oversight is non-negotiable.
Another major problem is deep-seated bias. AI models are trained on mountains of text and images from the internet, which, surprise, is full of human biases. If the training data reflects stereotypes about gender, race, or culture, the AI will learn and reproduce those same biases. This can result in outputs that are unfair, stereotypical, or just plain offensive.
And finally, you have the rise of deepfakes and misinformation. The same tech that creates stunning art can also be used to generate hyper-realistic but fake images, videos, and audio clips. It's a powerful tool for anyone looking to spread false information or create malicious content.
Generative AI Pros vs Cons
To put it all in perspective, here's a quick rundown of the main advantages and disadvantages you'll want to keep in mind when working with these tools.
| Benefits (Pros) | Limitations (Cons) |
|---|---|
| Drastic Time Savings: Automates repetitive and time-consuming tasks. | Factually Unreliable: Prone to "hallucinations" and making up information. |
| Creative Catalyst: Helps overcome creative blocks with new ideas and variations. | Inherent Bias: Can perpetuate and amplify biases found in its training data. |
| Scalable Personalization: Delivers tailored content and experiences to individuals. | Ethical Risks: Potential for misuse in creating deepfakes and misinformation. |
| Cost Reduction: Lowers operational costs by handling tasks once done by humans. | Lacks Common Sense: Cannot understand context, nuance, or ethics like a human can. |
| Accessibility: Makes complex tasks like coding or design more accessible to non-experts. | Requires Human Oversight: Outputs always need to be verified and reviewed by a person. |
Ultimately, the key is to lean into the benefits while actively guarding against the risks.
Your 3-Step Playbook for Using AI Responsibly
Knowing the risks is half the battle. The other half is doing something about it. Here are three simple, practical habits you can build to use generative AI tools without falling into the common traps.
- Always Fact-Check and Verify. Seriously, always. Treat any factual claim an AI makes as a starting point, not the final word. If it gives you a statistic, a historical date, or a quote, your very next move should be to confirm it with a trusted source. Don't ever copy-paste a fact from an AI into an important document without vetting it first.
- Write Better Prompts to Fight Bias. You have more control than you think. Instead of a vague prompt like "a photo of a CEO," which will likely produce a stereotypical image, get specific. Try something like, "a team of diverse executives, including men and women from various ethnic backgrounds, collaborating in a modern office." A well-crafted prompt can guide the AI toward a more inclusive and accurate result.
- Keep a Human in the Loop. The golden rule. For any high-stakes decision, AI should be your co-pilot, not the one flying the plane. Use it to generate drafts, analyze data, or suggest options, but the final judgment call has to come from a human. That's how you ensure that critical thinking, ethics, and plain old common sense—things AI just doesn't have—remain part of the process.
The Future of Generative AI
So, where is all of this heading? What does the future of generative AI actually look like?
Right now, we're watching the technology evolve past simple, one-trick tools. The next generation of AI won't just be about creating a picture or writing some text; it will be about integrated, intelligent systems that weave themselves seamlessly into our daily routines. We're on the brink of models that can see, hear, and speak all at once, and even autonomous assistants that can just get things done for you.
This shift is already happening. The focus is moving toward making our interactions with AI feel completely natural and a whole lot more powerful. It’s less about us learning how to write the perfect prompt for a machine and more about the machine learning how to understand and even anticipate what we need.
The Rise of Multimodal Models
The next big leap for generative AI is multimodal. This just means that a single AI model will be able to understand and work with different formats—text, images, audio, video—all at the same time. Think about giving an AI a written script, a folder of photos, and a voice clip, and then asking it to spin up a short, narrated video. That's where we're going.
Here’s a simple way to picture how it works:
- Step 1 Input: You snap a picture of your living room and upload it.
- Step 2 Prompt: You ask the AI, "Based on this photo, show me three different color palettes and make a shopping list for furniture that matches this style."
- Step 3 Output: The model looks at your photo, creates visual mockups of the room with new designs, and spits out a text-based shopping list.
This ability to jump between different kinds of data makes AI feel less like a tool and more like an intuitive creative partner.
The goal is to break down the barriers between different content types. An AI that can listen to a melody and generate a painting inspired by it is a much more capable assistant.
Ultimately, this shift is going to make ambitious creative projects accessible to everyone. You won't need to be a pro with a dozen different software tools—you'll just need to describe your vision to one incredibly versatile AI.
Introducing Autonomous AI Agents
Beyond just understanding different media, we're seeing the emergence of AI agents. The best way to think about an AI agent isn't as a tool you command, but as an autonomous assistant you can delegate tasks to. These agents are designed to handle complex, multi-step jobs all on their own.
For example, you could tell an agent: "Plan a weekend trip to Austin for two people next month. Find the best flights, book a pet-friendly hotel near downtown, and put together an itinerary with three good dinner spots."
The agent would then get to work:
- Searching for flights and comparing all the prices.
- Researching hotels that fit your criteria and booking one.
- Finding top-rated restaurants and building out a schedule.
- Presenting you with the final plan for a quick approval.
This represents a huge change in how we think about AI—from a content generator to a problem solver. The key is to stay curious, because this field is advancing in some truly incredible ways.
Ready to create stunning visuals with the power of AI? With AI Photo HQ, you can generate professional photoshoots, restore old pictures, and explore endless artistic styles in seconds. Start bringing your ideas to life today.